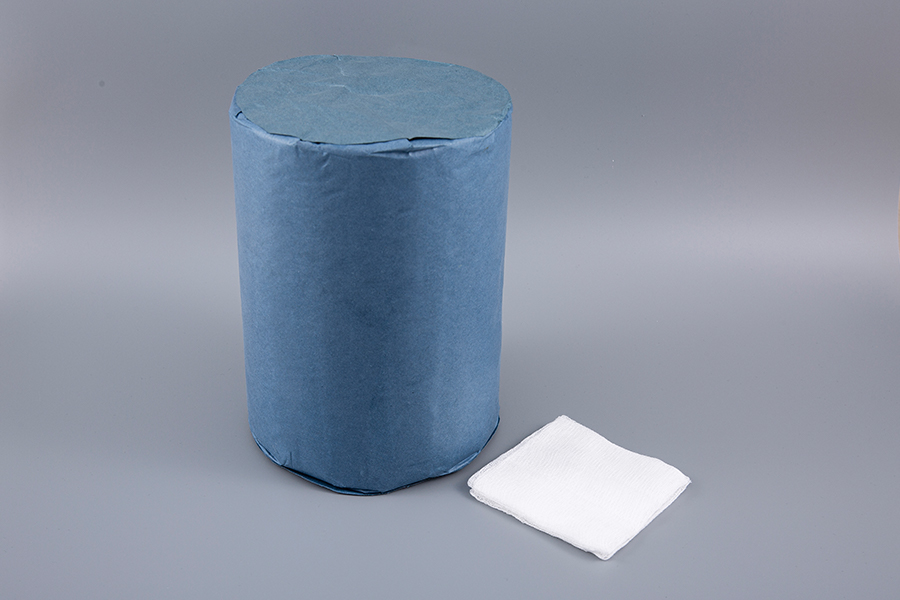
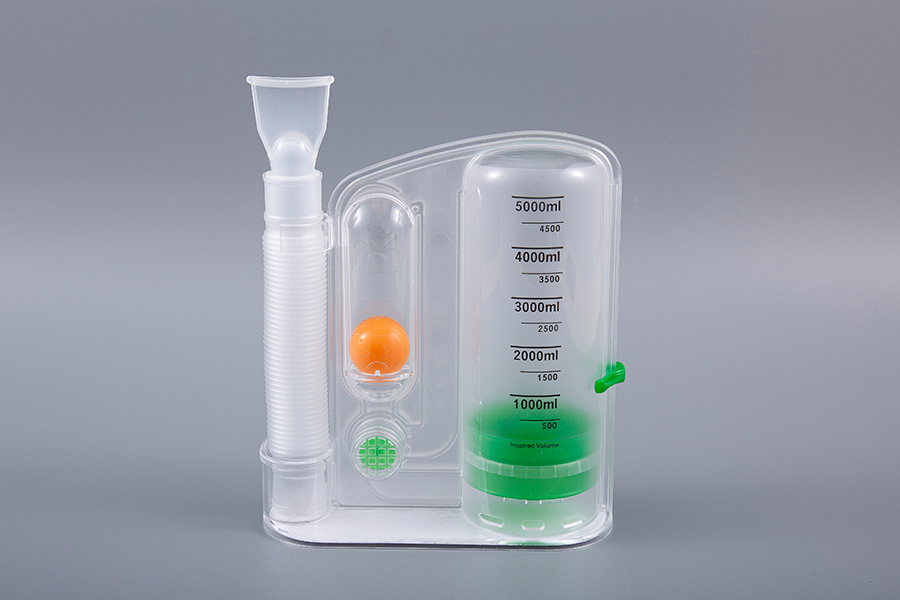
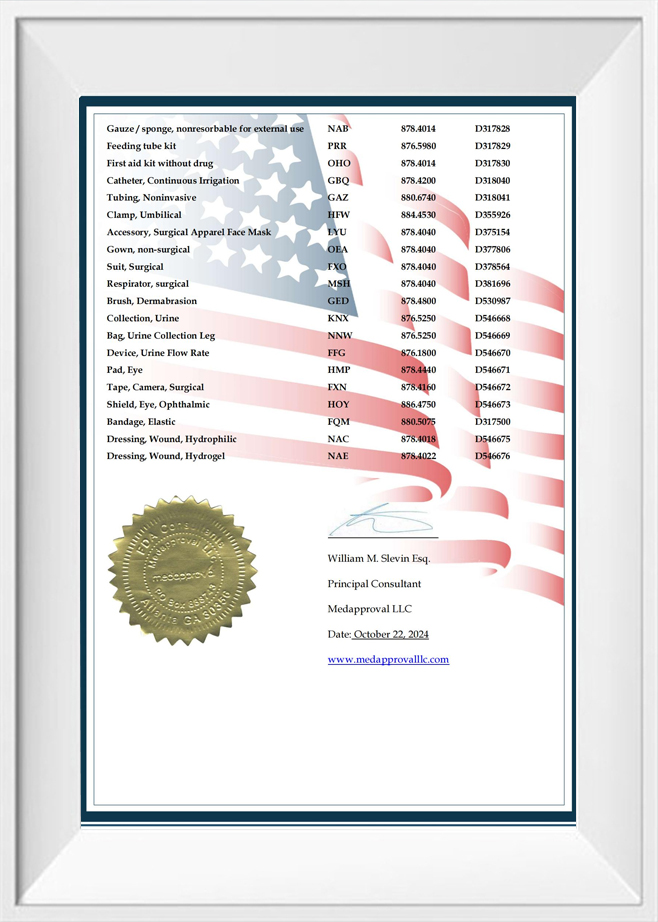
Founded in 2002, Suzhou Texnet is a China-based supplier specializing in high-quality medical disposable products. Located in Suzhou Industrial Park, just an hour's drive from Shanghai. We pride ourselves on holding CE and ISO 13485 certifications by TUV. We’re also FDA registered. As Spirometer for Diagnosing Respiratory Diseases Suppliers, our products are trusted by hospitals, pharmacies, and nursing homes across Europe, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, North America, and South America.
Over the past three decades, Suzhou Texnet has grown from a small startup into a key player in the global medical supply industry, achieving significant increases in yearly turnover. As a comprehensive one-stop solution provider, Professional Spirometer for Diagnosing Respiratory Diseases Company in China, we offer a broad range of products and services to meet all your medical disposable needs, simplifying the procurement process, combining the shipment, and ensuring consistent quality.
We view every client inquiry as an opportunity to demonstrate our commitment to quality. Our dedicated QC team ensures that all products meet established standards, while our customer service team is responsive to every piece of feedback or concern. .
At Suzhou Texnet, we focus on enhancing the client purchasing experience through continuous internal performance assessments. We supply Spirometer for Diagnosing Respiratory Diseases Custom. Our ultimate goal is to ensure that our clients enjoy doing business with us, helping them achieve greater success and profitability.
We look forward to partnering with you and achieving shared success.
Define What Your Worksite First Aid Station Must Handle When customers ask me for a worksite first aid station supply setup, I start with o...
READ MORE
 English
English Français
Français Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى